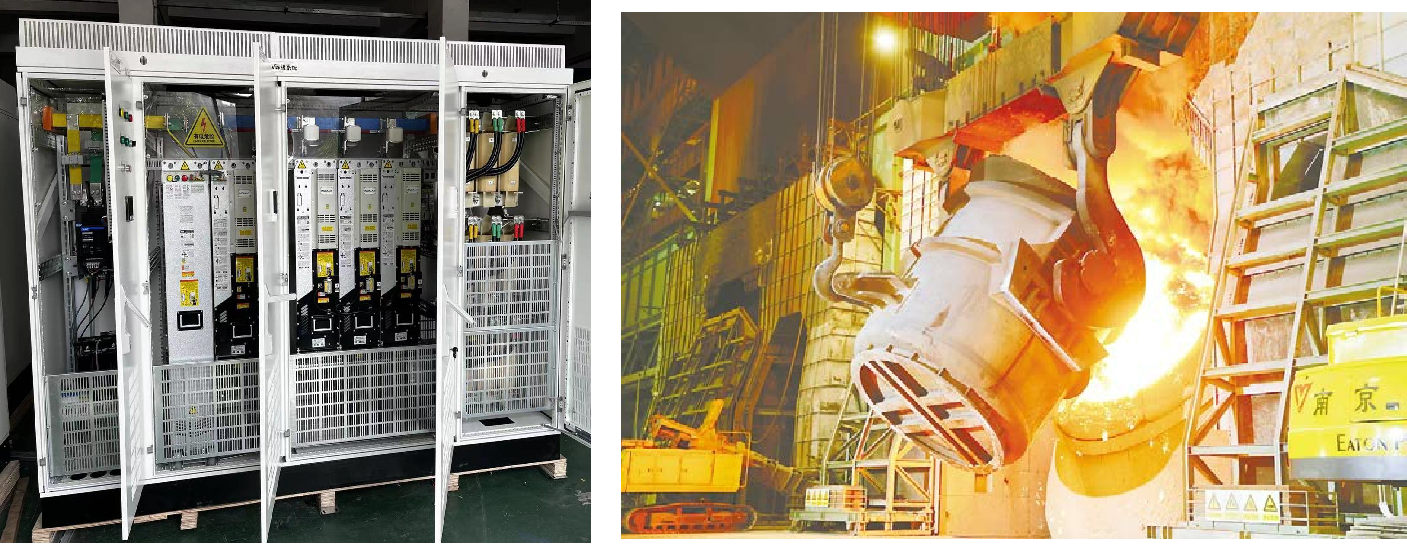
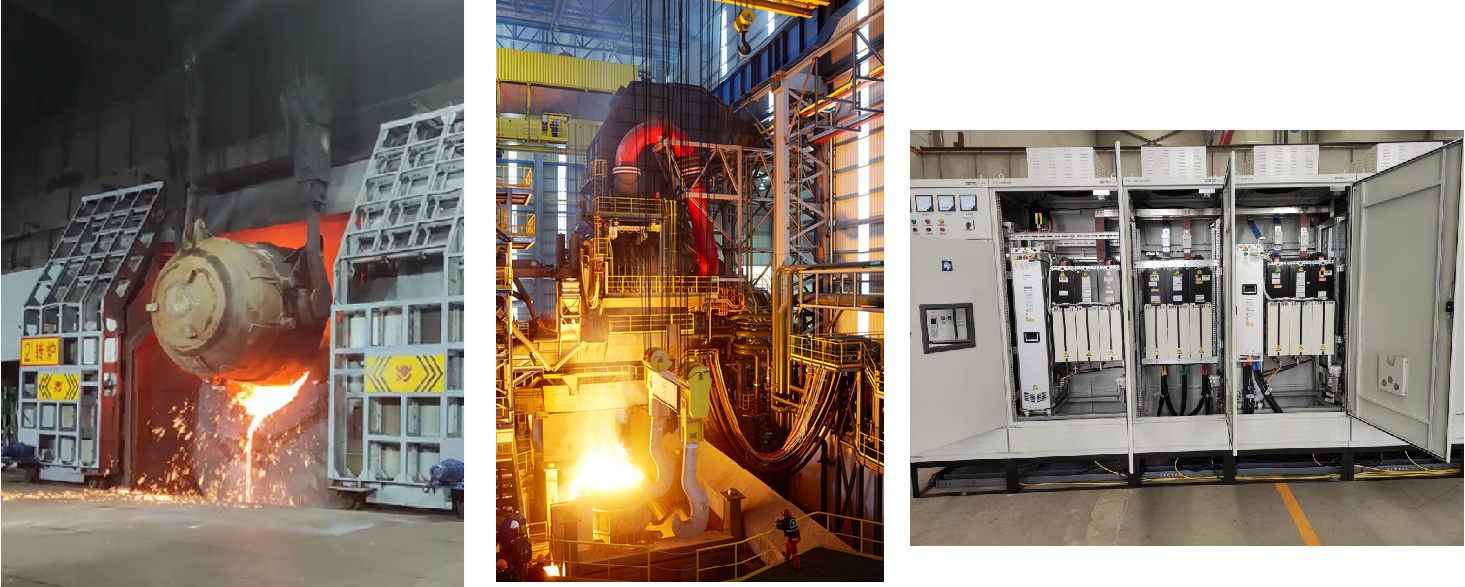
Selecting the appropriate Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable operation in various applications. Here are the steps and considerations involved in the selection process:
1. Determine the Load Characteristics
- Load Type: Identify whether the load is constant torque (like conveyor belts), constant power (like machine tool spindles), or variable torque (like fans and pumps).
- Torque Requirements: Understand the starting, continuous, and overload torque requirements of the load.
2. Match the Motor Specifications
- Motor Current: The VFD must be able to handle the motor’s full-load current continuously.
- Motor Voltage: The VFD’s output voltage must match the motor’s rated voltage.
- Motor Power: While the motor’s power rating gives an indication, the selection should primarily be based on the actual working current.
3. Consider Environmental Factors
- Temperature: The ambient temperature and cooling requirements will influence the size and type of VFD.
- Dust and Corrosion: Environments with high dust levels or corrosive agents may require special protection or sealing.
4. Control Objectives
- Speed Control: Determine the desired speed range and the method of control (e.g., V/f control, sensorless vector control, closed-loop vector control).
- Performance Requirements: Consider the acceleration/deceleration times and dynamic response needed.
5. Harmonic and EMI Mitigation
- Harmonic Filters: Depending on the VFD’s switching frequency and the sensitivity of the electrical system, harmonic filters may be necessary.
- EMI Suppression: Shielding and filters may be required to prevent electromagnetic interference with other equipment.
6. Safety and Protection
- Overload Protection: Ensure the VFD has adequate protection against overloads and short circuits.
- Safety Interlocks: Consider any necessary safety interlocks or fail-safe operations.
7. Compatibility with Other Equipment
- Communication Protocols: If the VFD is part of a larger control system, ensure compatibility with existing protocols.
- Integration with PLCs or SCADA systems: Check if the VFD can communicate and integrate smoothly.
8. Economic and Operational Considerations
- Cost: Evaluate the initial investment versus long-term operational savings.
- Maintenance: Consider the ease of maintenance and availability of replacement parts.
9. Technical Support and Warranty
- Service Availability: Check for local technical support and warranty terms.
- Brand Reputation: Opt for reputable manufacturers with proven track records.
10. Regulatory Compliance
- Standards and Certifications: Ensure the VFD complies with relevant electrical codes and safety standards.
Following these guidelines will help you choose a VFD that is well-suited for your specific application and operating environment. It’s often beneficial to consult with experts or the VFD manufacturer for tailored recommendations based on your unique requirements.